3-Axis CNC vs 5-Axis CNC: The Right Choice for Your Needs
Introduction
CNC(Computer Numerical Control) technology has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled precision and efficiency. Among the various types of CNC machines, 3-axis and 5-axis CNC systems are two of the most commonly used. But which one is right for your project? In this blog post, we'll dive deep into the world of 3-axis and 5-axis CNC, exploring their differences, advantages, and drawbacks to help you make an informed decision.
Basics of 3 – Axis and 5 – Axis CNC
3 – Axis CNC: The Fundamental Player
A 3-axis CNC machine operates on three linear axes: X, Y, and Z. These axes allow the machine to move the cutting tool or the workpiece in three perpendicular directions. This basic setup enables it to perform operations like milling flat surfaces, drilling holes, and cutting simple 2D shapes. It's the go-to choice for simple parts with straightforward geometries because of its ease of operation and programming. For example, in small-scale woodworking or basic metal part fabrication, a 3-axis CNC can quickly and accurately produce the desired components.
5 – Axis CNC: Unleashing Multidimensional Precision
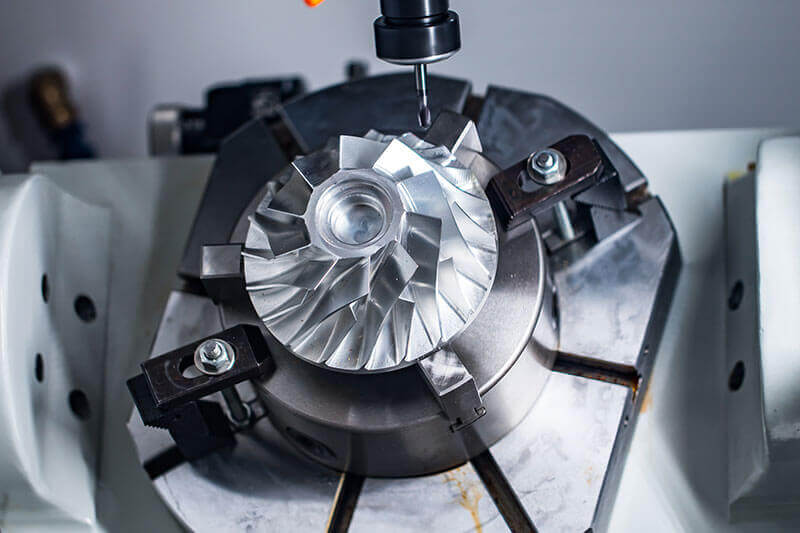
In contrast, a 5-axis CNC machine builds on the 3-axis foundation by adding two additional rotary axes. These rotary axes can be either A and B, or B and C, depending on the machine configuration. The extra axes provide the ability to machine parts from multiple angles without repositioning the workpiece. This means it can handle complex 3D shapes, intricate contours, and multi-sided components in a single setup. It's a game-changer for industries that require high precision and complex geometries, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Advantages of 3 – Axis CNC
Cost – Effective Solution
One of the biggest advantages of 3-axis CNC machines is their affordability. The initial purchase cost of a 3-axis CNC is significantly lower compared to a 5-axis model. Additionally, maintenance costs are also more manageable. This makes 3-axis CNCs an attractive option for small businesses, hobbyists, or anyone with a tight budget. You can start your manufacturing projects without breaking the bank.
Easier Programming and Operation
Programming a 3-axis CNC is relatively straightforward. The basic movements along the X, Y, and Z axes are easy to understand and code. Even those new to CNC technology can quickly get up to speed with the programming software. As a result, the training time for operators is minimal. This simplicity means you can start production faster and with less hassle.
Suitability for Specific Industries and Applications
3-axis CNC machines are well-suited for several industries. In the furniture manufacturing industry, they can be used to cut and shape wooden panels for tables, chairs, and cabinets. In the sign-making business, they are perfect for carving letters and designs into materials like acrylic or wood. Their simplicity and reliability make them a workhorse for these types of applications.
Advantages of 5 – Axis CNC
Enhanced Precision and Complexity
5-axis CNC machines offer superior precision when it comes to machining complex parts. The ability to control the cutting tool from multiple angles ensures that it maintains the optimal cutting position throughout the process. This results in higher quality finishes and tighter tolerances. For instance, in the production of turbine blades for jet engines, 5-axis CNCs can accurately create the intricate shapes and curves required, ensuring maximum efficiency and performance.
Time – Saving and High Productivity
With a 5-axis CNC, you can complete multiple machining operations in a single setup. Instead of having to reposition the workpiece several times on a 3-axis machine, a 5-axis CNC can access all the required surfaces without any additional setup. This not only saves time but also reduces the chances of errors caused by repositioning. As a result, production cycles are shorter, and overall productivity is significantly increased.
Versatility in Design and Manufacturing
The added axes of a 5-axis CNC open up a world of design possibilities. Designers can create more complex and innovative products that would be impossible or extremely difficult to produce with a 3-axis machine. In the automotive industry, 5-axis CNCs are used to manufacture engine components, transmission parts, and custom body panels. This versatility allows manufacturers to stay ahead of the competition by offering unique and high-quality products.
Disadvantages of 3 – Axis CNC
Limited to Simple Shapes
While 3-axis CNCs are great for simple parts, they struggle with complex geometries. Machining parts with multiple angles or intricate 3D shapes often requires multiple setups. Each setup adds time and increases the risk of errors. This limitation can make it challenging to meet the demands of projects that require more complex designs.
Lower Efficiency for Complex Parts
For complex parts, 3-axis CNCs are less efficient. The cutting tool has limited access to the workpiece, which means longer toolpaths and more time spent on each operation. This inefficiency can lead to higher production costs and longer lead times, making them less suitable for projects with tight deadlines or high-volume production requirements.
Disadvantages of 5 – Axis CNC
High Initial Investment
5-axis CNC machines come with a hefty price tag. Not only is the cost of the machine itself much higher than a 3-axis model, but you also need to invest in specialized software and cutting tools. This high initial investmen
t can be a significant barrier for many businesses, especially those just starting out or with limited financial resources.
Complex Programming and Skilled Operator Requirement
Programming a 5-axis CNC is a complex task. It requires a deep understanding of the additional rotary axes and how they interact with the linear axes. Moreover, operating a 5-axis CNC machine demands highly skilled operators. Finding and training such operators can be difficult and expensive. This complexity can slow down the production process and increase operational costs.
How to Decide: 3 – Axis or 5 – Axis?
Analyzing Your Project Requirements
The first step in choosing between a 3-axis and 5-axis CNC is to analyze your project requirements. Consider factors such as the complexity of the part, the required precision, the production volume, and the materials you'll be working with. If your project involves simple, flat parts with basic geometries, a 3-axis CNC will likely suffice. But for complex, multi-sided parts with tight tolerances, a 5-axis CNC is the better choice.
Budget Considerations
Your budget plays a crucial role in this decision. If you're on a tight budget, a 3-axis CNC offers a more cost-effective entry into CNC machining. However, if you have the financial resources and your projects demand the capabilities of a 5-axis machine, the long-term benefits may outweigh the initial investment.
Skill Level of Your Team
The skill level of your team is another important factor. If your operators are new to CNC technology, starting with a 3-axis CNC and gradually building up their skills may be the best approach. But if you have a team of experienced CNC programmers and operators, a 5-axis CNC can be a valuable addition to your manufacturing capabilities.
Real – World Examples
Case 1: 3 – Axis CNC in a Small – Scale Workshop
A small – scale metalworking workshop was approached with an order to produce 100 simple metal brackets. With a limited budget and a team of operators new to CNC, they decided to use their 3-axis CNC machine. The straightforward programming and operation of the 3-axis CNC allowed them to quickly set up the job and start production. They were able to complete the order on time and within budget, proving that a 3-axis CNC is a great choice for small, simple projects.
Case 2: 5 – Axis CNC in Aerospace Manufacturing
An aerospace company needed to produce a batch of high-precision turbine blades. The complex shape and tight tolerances of the blades made a 5-axis CNC machine essential. The 5-axis CNC was able to machine the blades in a single setup, achieving the required precision and surface finish. This not only saved time but also ensured the quality and performance of the final product, highlighting the importance of 5-axis CNCs in high-precision manufacturing industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machines have their own unique strengths and weaknesses. The right choice depends on your specific project requirements, budget, and the skill level of your team. By understanding the differences between these two types of CNC systems, you can make an informed decision that will optimize your manufacturing processes and drive the success of your projects. Have you used either 3-axis or 5-axis CNC in your work? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below!