what is the Lightweight Metals?
Lightweight metals play a vital role in modern manufacturing. With the continuous improvement of product performance requirements in the modern manufacturing industry, lightweight has become the goal pursued by many industries such as aerospace and automotive. Components made of lightweight metals in these fields show excellent characteristics such as high strength, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, etc., which is of great significance for weight reduction.
In the field of CNC machining, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, titanium alloy and other lightweight metal applications are very extensive, for example, the use of modern aircraft aluminum alloy more than 70% of the weight of the aircraft to reduce the weight of each kilogram, can greatly save fuel consumption, reduce operating costs. In this article, we will discuss the characteristics, advantages and application cases of common lightweight metals in CNC machining.
1、What is Lightweight Metals?
Lightweight metals are relatively low density metals that weigh less for the same volume. Their specific gravity is typically in the range of 1.5 – 5.0 grams per cubic centimeter, which is lower than common engineering materials such as steel (approximately 7.85 grams per cubic centimeter). This property is valuable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics, where it helps reduce weight to improve performance and fuel efficiency.
2、Lightweight Metals commonly used in CNC machining
(1) Aluminum Alloy
Aluminum alloy has good corrosion resistance because it forms a dense oxide film on its surface, which prevents oxygen and moisture from coming into contact with the internal metal and slows down corrosion. In CNC machining, if the surface is properly treated, such as through anodizing to form a thicker and stronger oxide film, the corrosion resistance can be further improved, significantly extending the service life of the product.
characterization
- It has a degree of 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter, a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and easy workability.
- Benefits: Aluminum provides vital structural support without adding significant weight, making it ideal for applications in wet environments such as outdoor and marine. In addition, a variety of alloys such as 2024, 6061 and 7075 are available for specific applications.
Application Areas
Widely used in aerospace components (e.g., aircraft frames, wing structures), automotive parts (e.g., wheels, engine blocks), sports equipment (e.g., bicycle frames), and electronics housings (e.g., laptops, mobile devices).
(2) Titanium alloy
Titanium is strong, stronger than many traditional metals such as steel, yet much lighter, making it an ideal material for high-strength, low-weight applications such as the aerospace industry. In CNC machining, its high strength allows the manufacture of thinner, stronger parts that reduce overall weight, while its good toughness allows it to withstand machining stresses and resist fracture. The strength of titanium can reach more than 1000MPa, which is several times that of ordinary steel. Titanium parts perform reliably under high loads, ensuring product safety.
characterization
- Density 4.43 g/cm³, high tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, difficult machinability, requires special tools.
- Benefits: Titanium has a higher strength per unit weight than most metals, is suitable for high stress applications, retains its strength at elevated temperatures, and its natural oxide layer has excellent corrosion resistance (especially in salt water and acidic environments).
- Areas of application:Used in aerospace (e.g., turbine engines, structural components), medical (e.g., implants, prosthetics), marine (e.g., propeller shafts, fittings), high-performance automotive (e.g., exhaust systems).
(3) Magnesium Alloy
Magnesium is currently the lightest structural metal available, making it attractive to weight-sensitive industries. However, magnesium alloys are more difficult to work with than aluminum and titanium and are more susceptible to corrosion if not handled properly.
characterization
- Density 1.738 g/cm³, medium strength to weight ratio (lighter than aluminum but weaker), medium corrosion resistance (need coatings or alloys to improve corrosion resistance), medium workability (need to be careful because of flammability).
- Benefits: Magnesium’s low density makes it the first choice for weight-saving critical applications, and although weaker than aluminum and titanium, it still has good strength in many applications and is more cost-effective than some lightweight materials.
- Areas of application:Applications include automotive (e.g., engine blocks, transmissions), aerospace (e.g., aircraft seats, mounts), and consumer electronics (e.g., laptop housings, mobile devices).
(4) Beryllium
Beryllium is an advanced lightweight metal commonly used in highly specialized applications. It is more expensive and difficult to machine than aluminum or titanium, but its unique properties make it extremely valuable in specific industries. Beryllium’s high strength, low density and excellent thermal properties make it the material of choice for high performance applications.
characterization
- Density 1.848 g/cm³, very high strength (stronger than many other lightweight metals), high corrosion resistance (especially at high temperatures), difficult workability (requires specialized equipment and safety precautions).
- Benefits: Beryllium is stronger and more stable at high temperatures than other lightweight metals, and can be used in high-performance thermal systems such as heat exchangers, and its high hardness makes it an ideal material for making precision components.
- Application Areas:
Used in aerospace (e.g., satellite components, structural parts), nuclear energy (e.g., reactors, radiation shielding), electronics (e.g., connectors, electrical contacts).
(5) High strength steel alloys (e.g. 4130, 4340)
Strength and weight characteristics
While steel is typically heavier than other lightweight materials, some high-strength steel alloys offer a good balance of strength and weight, and are especially suited for components subjected to extreme stress and wear. The high strength of steel makes it an ideal choice for heavy machinery and structural components.
Features & Benefits
- Properties: Density 7.85 g/cm³ (heavier than other lightweight metals), very high tensile and yield strengths, medium corrosion resistance (requires coating or treatment), medium to difficult workability (may require specialized tools).
- Benefits: Steel alloys such as 4130 (chromium-molybdenum) and 4340 (nickel-chromium) are extremely strong in tensile strength, steel is less expensive than specialty materials such as titanium or beryllium, and is resistant to abrasion and can be treated to increase toughness.
- Areas of application:For landing gear, structural components and fasteners, anti-roll bars, chassis components and suspension systems, as well as heavy machinery and tools requiring high strength.

3、Considerations for the selection of Lightweight Metals
The selection of lightweight metals for CNC machining requires a combination of strength requirements, corrosion resistance, machinability and cost.
Aluminum alloys are balanced and commonly used; titanium alloys have excellent strength and temperature resistance but are costly; magnesium alloys are suitable for weight-sensitive applications; and beryllium is suitable for highly specialized applications.
4、Reasons for choosing Lightweight Metals
(1) Improved fuel efficiency and performance
In industries such as aerospace, automotive and transportation, the use of lightweight metals to reduce the weight of products directly improves fuel efficiency and performance. Lightweight metals such as aluminum, magnesium and titanium reduce the total weight of the end product and reduce the energy required to move or operate it.
(2) Corrosion resistance and long life
Lightweight metals such as aluminum, titanium and magnesium alloys have excellent corrosion resistance, which is critical for material applications exposed to harsh environments. Good corrosion resistance extends product life and reduces long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
(3) Improvement of machinability
Lightweight metals are often selected for their machinability, which is the ease with which the material can be machined in processes such as CNC machining, milling and turning. Many lightweight metals, such as aluminum, have relatively simple machining requirements that can reduce production time and labor costs.
(4) Sustainability
Sustainability is increasingly emphasized in all industries, and lightweight metals can help enhance the environmental credentials of a project. Reducing the weight of products improves energy efficiency during use and reduces the environmental impact of transportation and production.
(5) Multifunctionality
Lightweight metals are versatile and suitable for a wide range of industries. Whether it’s a durable component for the high-tech industry or a lightweight material for consumer goods, there is a wide range of needs to be met.
(6) Application-specific
Lightweight metals can often be alloyed with other materials to enhance specific properties. Aluminum, for example, can be alloyed with copper, magnesium or silicon to improve strength, corrosion resistance or thermal conductivity, allowing manufacturers to select the ideal material for their project requirements.
5、Lightweight Metals comparison table
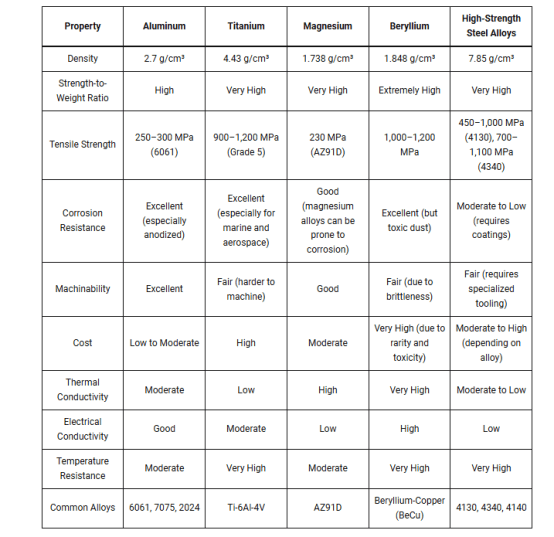
conclude
Selecting a lightweight metal for CNC machining requires a combination of factors, including performance requirements, environmental conditions and machinability. Metals such as aluminum, titanium and magnesium have their own advantages in different applications, and careful evaluation of these factors allows manufacturers to select the ideal material to achieve a balance of strength, weight and cost. When in doubt, consult a Xavier CNC machining professional to ensure the right metal is selected for optimum performance and efficiency.






