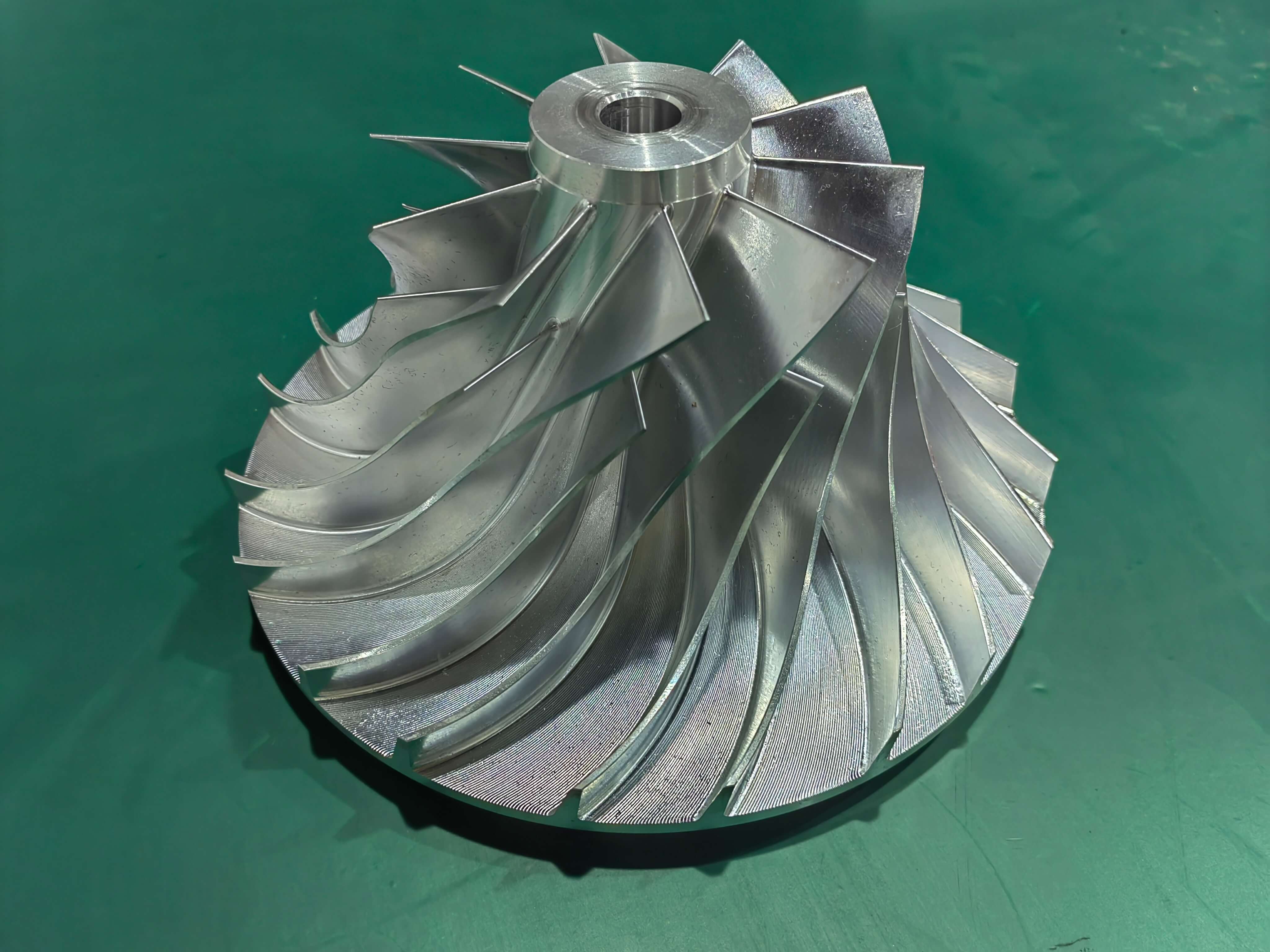
Complete Guide to milled parts: types, advantages and designs
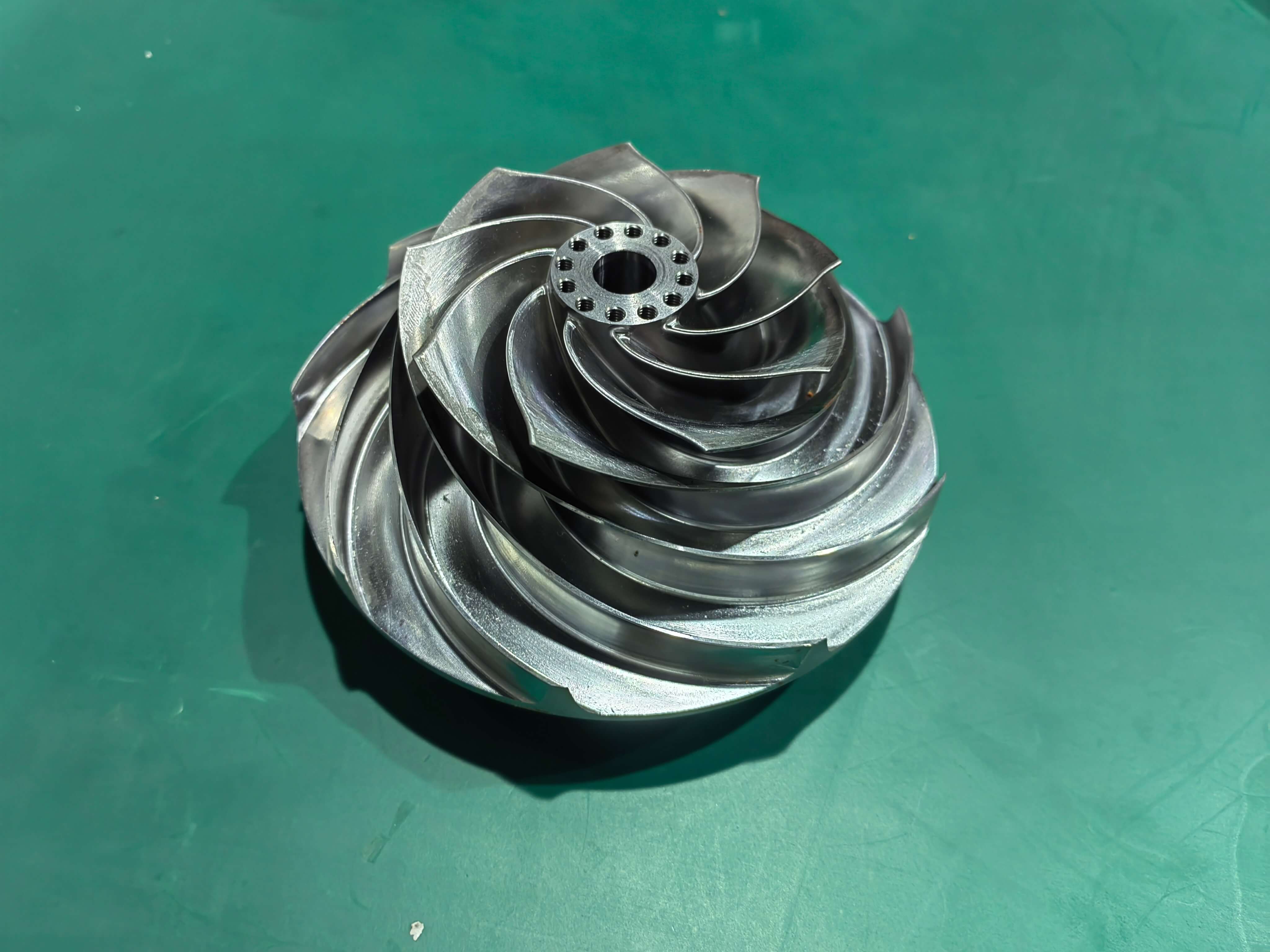

What are milled parts?
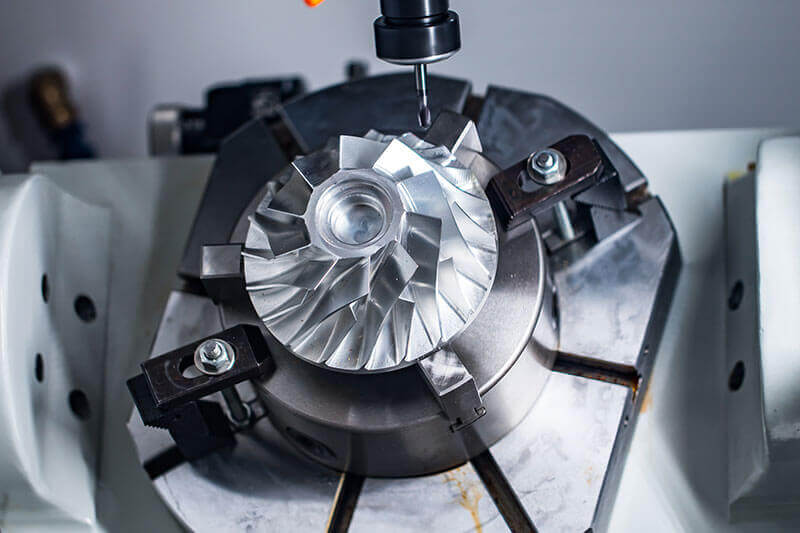
Milled parts are components crafted through the milling process. Milling is a machining technique where a rotating cutting tool, such as an end mill or a face mill, removes material from a workpiece. This process can create a diverse range of shapes, from simple flat surfaces to highly complex geometries. The cutting tool moves in multiple axes, allowing for the production of parts with various features like slots, pockets, and intricate contours.
There are two main types of milling: manual and computer – numerical – control (CNC) milling. In manual milling, a skilled machinist controls the movement of the cutting tool and the workpiece by hand. It requires a high level of expertise but can be useful for small – scale or custom jobs. On the other hand, CNC millingaerospace is more common for complex and large – scale production. With CNC milling, a computer program controls the movement of the cutting tool, ensuring high precision and repeatability.
Why use milled parts?
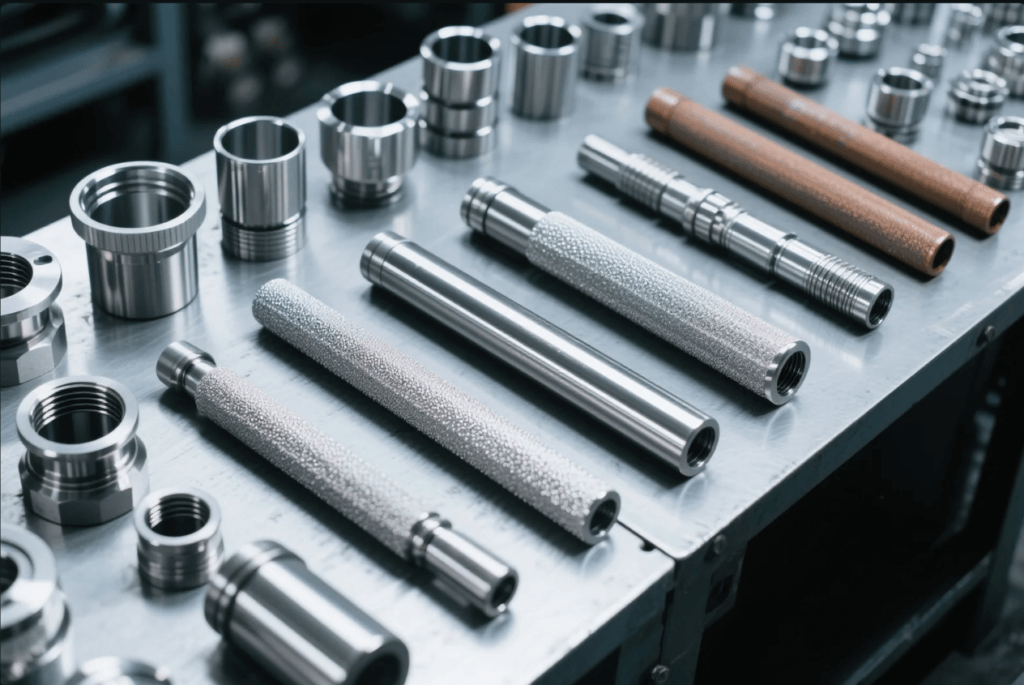
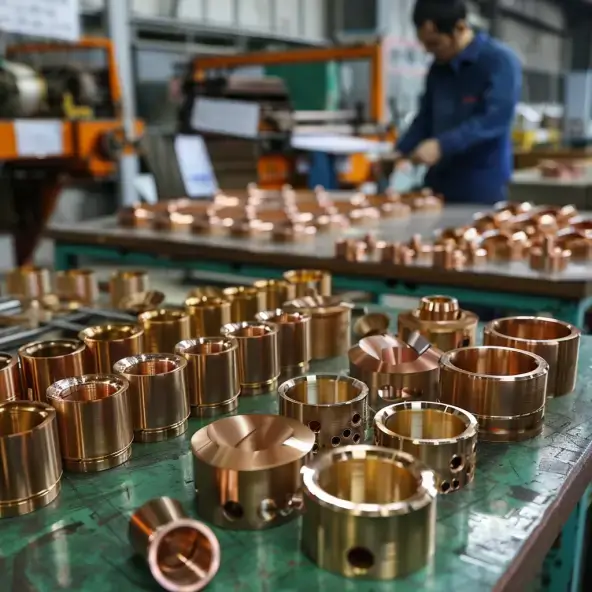
Milled parts offer several compelling reasons for their use. Firstly, they can be made from a wide variety of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics and composites. This material flexibility allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable material based on the part’s intended application, such as strength requirements, weight considerations, or chemical resistance.
Secondly, milled parts can achieve high precision. The milling process can meet tight tolerances, which is crucial for parts that need to fit together accurately, like components in engines or mechanical devices. Additionally, milled parts can have detailed features. Whether it’s a tiny groove or a complex pattern, the milling process can bring the design to life, making it ideal for parts with intricate designs.
What are the advantages of milled parts?
No minimum order quantity
One of the significant advantages of milled parts is the lack of a minimum order quantity. Unlike injection – molded parts, which often require expensive tooling and a large – scale production run to be cost – effective, milled parts can be produced in small quantities, even just one piece. This is extremely beneficial for small businesses, startups, or for prototyping purposes. For example, if a company is developing a new product and needs to test a few different versions of a part, they can order small quantities of milled parts without breaking the bank.
Design freedom
Milled parts offer extensive design freedom. CNC milling, in particular, can create parts with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods. There are fewer restrictions compared to processes like injection molding, which often require thin walls and specific design features for the mold – making process. With milling, parts can have thick sections, sharp corners, and unique shapes. For instance, aerospace components often have complex, non – standard shapes that can be easily produced through milling.
Quality
The quality of milled parts is generally very high. The precision of the milling process, especially with CNC machines, ensures that each part is consistent. Manufacturers can control factors like the speed of the cutting tool, the feed rate, and the depth of cut to achieve the desired quality. Moreover, the surface finish of milled parts can be excellent, which is important for parts that need to be smooth for proper functioning, such as parts in a high – performance engine or a medical device.
Delivery time
Milled parts can be fabricated relatively quickly. Since there is no need for time – consuming and expensive tooling setup, as in injection molding, the production process can start almost immediately after the design is finalized. Modern CNC milling machines are also highly efficient, with some capable of rapid movement rates. This means that for small – scale production or prototyping, the delivery time for milled parts is often shorter compared to other manufacturing methods, allowing companies to get their products to market faster.
Surface finish
The surface finishconsumer product of milled parts is often superior to that of parts made by other methods. Milled parts can avoid common surface defects found in injection – molded parts, such as flow lines and flash. After milling, parts can be further processed, like through polishing or sanding, to achieve an even better surface finish. In contrast, 3D – printed parts, especially those made by FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), often have visible layer lines that require additional post – processing to smooth out.

How to design milled parts?
Designing milled parts requires careful consideration of several factors. First, it’s essential to understand the capabilities and limitations of the milling process. For example, the size of the cutting tool affects the minimum radius of curves and the width of slots that can be cut. Designers should avoid creating features that are too small or too complex for the available tools.
Wall thickness is another crucial factor. While milled parts can handle thicker walls better than injection – molded parts, extremely thin walls should still be avoided. If thin walls are necessary, it might be better to consider alternative manufacturing methods. Additionally, when designing holes and cavities, their depth and diameter should be within the capabilities of the cutting tools. Holes should be sized to match standard drill bit diameters whenever possible to simplify the machining process.
Protrusions and undercuts also need to be designed with care. Tall protrusions can be difficult to machine due to tool vibrations, so their height should be limited relative to their width. Undercuts, which are areas that cannot be accessed by a standard cutting tool, may require special tools or machining techniques. If possible, it’s best to avoid undercuts to simplify the manufacturing process and reduce costs.
What are the applications for milled parts?
Milled parts have a wide range of applications across various industries. In the automotive industry, they are used for engine components, transmission parts, and custom – made brackets. Engine blocks, for example, require high – precision milling to create the complex internal structures that are essential for the engine’s performance.
In the aerospace industry, milled parts are crucial for manufacturing aircraft components such as wing spars, engine mounts, and landing gear parts. These parts need to be lightweight yet extremely strong, and the milling process can meet these requirements by using advanced materials and precise machining techniques.
The medical field also benefits from milled parts. Implants, surgical instruments, and medical device components are often made through milling. For example, titanium implants can be milled to fit the unique anatomy of a patient, ensuring a better fit and reduced risk of rejection.
In consumer products, milled parts can be found in items like smartphones, laptops, and high – end kitchen appliances. The casings, connectors, and internal components of these products often require the precision and quality that milling can provide to ensure smooth operation and an attractive appearance.
How do I outsource milled parts?
Outsourcing milled parts can be a cost – effective and efficient option, especially for companies that don’t have in – house machining capabilities. When choosing an outsourcing partner, start by looking for companies with relevant experience and a good reputation.
Certifications can be a useful indicator of a company’s quality and reliability. ISO certifications, for example, demonstrate that the company follows international standards for quality management. Word – of – mouth is also valuable. Talk to other companies in your industry that have outsourced milled parts and ask about their experiences with different manufacturers.
Once you’ve identified potential partners, communicate your requirements clearly. Ask for detailed quotes that include all costs, such as machining, finishing, and shipping. It’s also a good idea to visit the manufacturing facility if possible to see their equipment and processes firsthand. This can give you confidence in their ability to produce high – quality milled parts.
When outsourcing, make sure your design follows the guidelines for milling. Provide clear technical drawings and use universal standards to avoid misunderstandings. Also, consider signing a non – disclosure agreement to protect your intellectual property, especially if your design is unique or confidential.
Video Demonstration of Milled Parts Production
Watch the video above to see a real – life demonstration of how milled parts are produced. From the setup of the CNC milling machine to the final product, this video showcases the entire process, giving you a better understanding of the techniques and precision involved in creating milled parts.
Conclusion
Milled parts are a versatile and reliable option in manufacturing. Whether you’re a small – scale producer, a startup, or a large – scale manufacturer, understanding the types, advantages, design principles, applications, and outsourcing process of milled parts can help you make informed decisions. By leveraging the benefits of milled parts, you can create high – quality products that meet the demands of various industries.