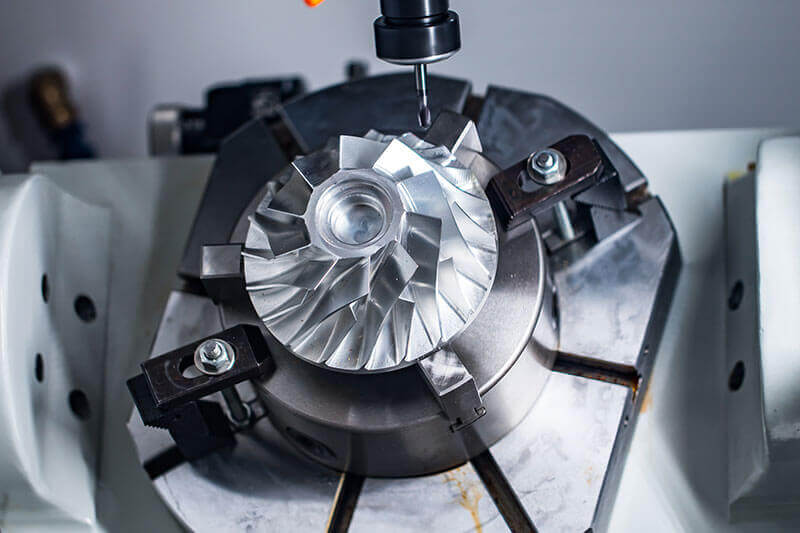
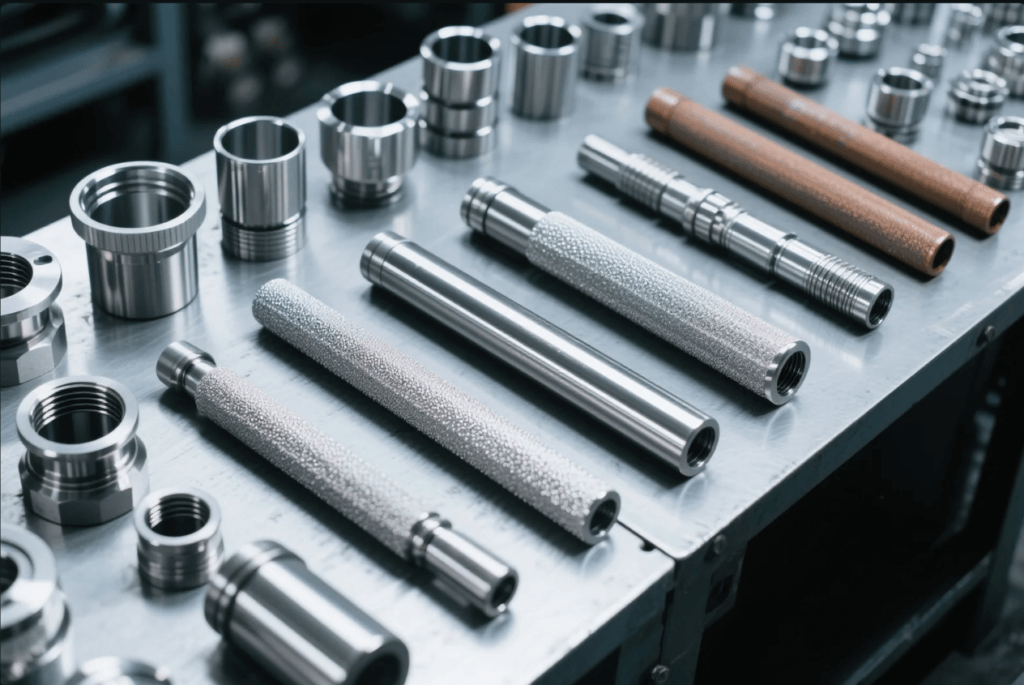
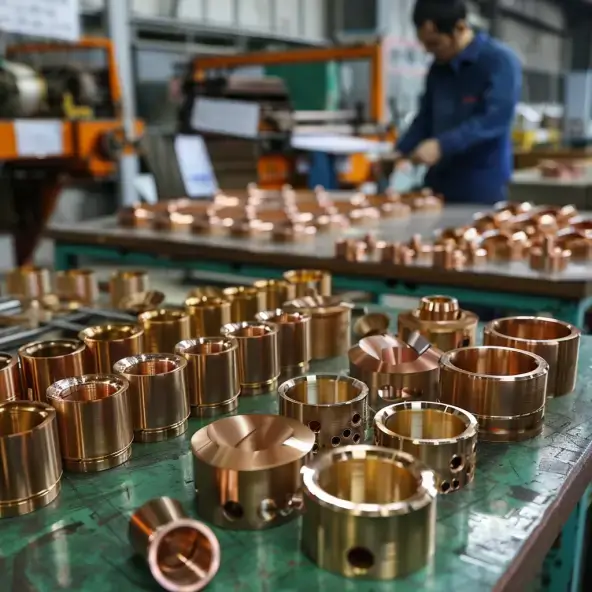
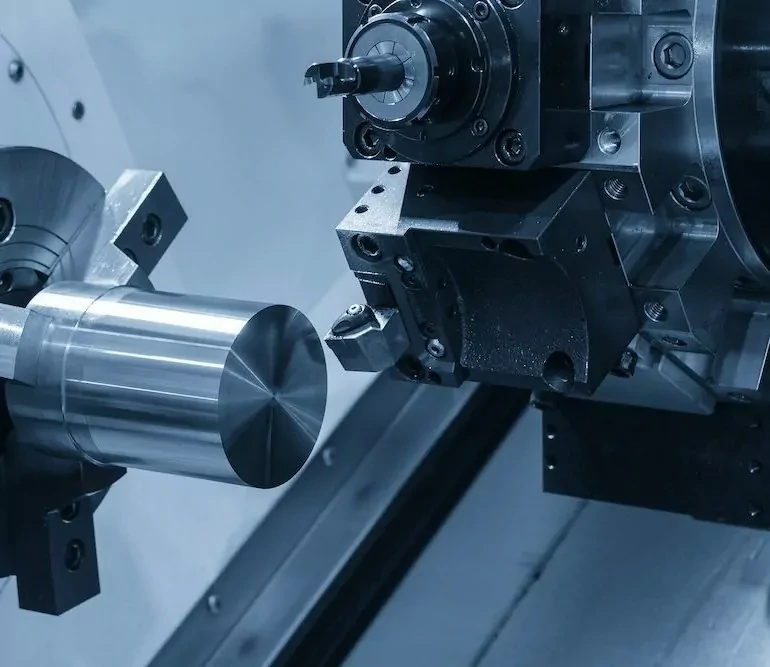
1、CNC Turning Basics: The Starting Point to Precision Manufacturing
The core principle of CNC turning
CNC turning (Computer Numerical Control Turning) uses the workpiece rotation as the main motion and the tool feed motion along the X and Z axes (and additional axes such as the C axis), and the G-code commands are converted into precise servo-motor displacements by the numerical control system. Compared with conventional turning, the positioning accuracy jumps from ±0.05mm to ±0.005mm, and the repeatability reaches ±0.002mm, enabling the machining of complex rotary structures such as spiral grooves and hyperboloidal surfaces. The automated tool change system and constant temperature machining environment further guarantee the consistency of accuracy in mass production.
Technology upgrade for precision CNC turning
Precision CNC turning reinforces the three core elements of basic CNC turning:
- Hardware precision: Adopting air-floating guideway and hydrostatic spindle, the mechanical vibration is controlled below 5μm;
- Control Precision: Nano-scale numerical control system (resolution 0.001μm) with laser interferometer real-time compensation of pitch error;
- 3. Environmental control: constant temperature (20 ± 0.5 ℃), constant humidity workshop with air purification system to eliminate thermal deformation and particle pollution effects.
2、Precision CNC Turning Material Selection: Balancing Performance and Processes

Precise adaptation of metallic materials
Titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V): It is the first choice for aviation because of its high strength (σb≥900MPa) and low density (4.5g/cm³). However, it is easy to deform with low modulus of elasticity, and requires PCD coated tool (Vc=80-120m/min) and low temperature cooling (-30℃ liquid nitrogen) to suppress vibration.
Nickel-based alloy (Inconel 718): excellent high-temperature strength (σb ≥ 1200MPa at 650°C), but the hardened layer reaches 0.2mm when cutting, so it is necessary to use ceramic tools (Vc = 50-80m/min) and to avoid chipping by a very small feed (f = 0.05mm/r).
3. Copper alloy (beryllium bronze): with high conductivity and fatigue resistance for precision connectors, easy to stick when turning, need to use coated tools (such as TiAlN) with high-pressure internal cooling (10MPa) chip removal.
Precision machining of non-metallic materials
Engineering ceramics (zirconia): hardness HV1200+, to be turned with a diamond wheel (line speed 200m/s), chipping prevented by micro-feed (0.005mm/rev).
PEEK polymer: high coefficient of thermal expansion, requires water-cooled spindle (<25℃) and very small depth of cut (0.1mm) to control deformation.
3、Precision CNC turning application industries
Engine components: the turbine shaft adopts five-axis turning to achieve 0.002mm wall thickness gradient structure, surface roughness Ra0.2μm, with ultrasonic vibration cutting to reduce residual stress by 30%.
2. Fuel system: The injector nozzle needle valve is controlled by precision turning with cylindricity ≤ 0.5μm, which ensures the fuel atomisation precision and improves the combustion efficiency by 5%.
Wafer clamping parts: Silicon Aluminium Alloy (SiC/Al) chucks are ultra-precision turned with flatness of 0.3μm and surface roughness of Ra0.05μm to meet the requirements of sub-nanometer positioning of wafers.
Photolithography equipment shaft system: The roundness error of tungsten carbide ceramic shaft is controlled within 0.1 μm, and with the magnetic fluid seal, it achieves the ultra-low speed (0.01 rpm) and stable operation in a clean environment.
Medical Device Industry
Cardiac stent delivery system: Nitinol guidewire is precision turned and then electrolytically polished to reduce the surface roughness to Ra0.02μm, reducing the risk of endothelial damage.
Neurosurgical electrodes: platinum-iridium alloy probes are turned and then micro-arc oxidised to form a nanoscale porous structure, enhancing biocompatibility and signal conduction efficiency.
4、Precision CNC turning surface treatment

Micron-scale surface quality enhancement
- Ultra-precision Turning Mirror Surface Processing: Using natural monocrystalline diamond tools (tip radius <0.1μm) to achieve a Ra0.02μm mirror surface effect at a depth of cut of 0.005mm, for the manufacture of optical mirror bases.
- Electrochemical polishing (ECP): For stainless steel parts, the surface roughness is reduced from Ra0.8μm to Ra0.1μm by removing a 0.003mm hardened layer, while eliminating stress concentrations caused by tool marks.
Functional coating deposition
- PVD coating technology: TiN-Ag composite coatings are deposited on the surface of titanium implants, combining antimicrobial properties (E. coli killing >99%) with a low coefficient of friction (μ=0.12).
- Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD): Growing diamond coatings on the surface of ceramic tools increases tool life by a factor of 5 when cutting high-temperature alloys.
Surface Enhancement Process
- Laser Shock Strengthening (LSP): Pulsed laser treatment of the surfaces of aerospace shaft components creates a 0.3mm compressive stress layer, increasing fatigue life by 200%.
- Ion injection: Nitrogen ions are injected into the surface of the mould steel to form a modified layer with a hardness of HV2000+, which increases the wear resistance by 8 times.
5、Future trends in precision CNC turning
Intelligent Processing Closed Loop
AI algorithms analyse cutting force and vibration data in real time to automatically optimise feed rate and tool paths, which was applied by a manufacturer to increase machining efficiency by 35% and reduce scrap rate to 0.1%.
Hybrid Manufacturing Technology Convergence
Turning and 3D printing composite, in situ additive manufacturing of gradient functional structures after turning and forming on titanium alloy substrates, with 40% higher material utilisation.
Green Precision Machining
Dry cutting with MQL (micro lubrication) technology reduces cutting fluid usage by 95% and meets the semiconductor industry’s ISO 14644-1 Class 1 cleanliness standard.
6、conclude
Precision CNC turning has gone beyond traditional machining to become a key link between materials science, CNC technology and high-end manufacturing. From the ‘heart’ of an aero-engine to the ‘nerves’ of a semiconductor device, this technology drives industrial innovation with micron-level precision. In the future, with the deep integration of nanoscale control, intelligent decision-making and green manufacturing, precision CNC turning will continue to provide manufacturing support for cutting-edge technologies. To discuss specific material process parameters or industry solutions, please feel free to communicate further.
FAQ
What materials can I use for CNC turning services?
Works with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics and composites.
How do I get a quote for CNC turning services?
You can easily request a quote by contacting SCZY LTD through their website or customer service.
Which industries benefit most from CNC turning services?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical and electronics benefit greatly from CNC turning services because of their precision and versatility.
Is SCZY LTD committed to sustainable development?
Yes, SCZYLTD is actively involved in sustainability programmes and uses environmentally friendly materials and processes wherever possible.
How does SCZYLTD ensure the quality of its CNC turned parts?
SCZY LTD uses advanced inspection tools and stringent quality control processes to ensure that components meet the required specifications.